
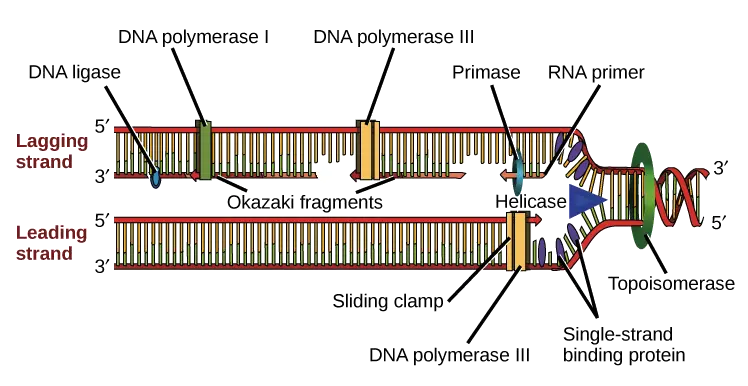
New nucleotides are added one by one to the end of growing strand by an enzyme called DNA polymerase. The choice of nucleotides to be added in the new strand is dictated by the sequence of bases on the template strand. The next step involves the addition of new complementary strands. The synthesis of new daughter strands is initiated at the replication fork. Before the DNA synthesis begins, both the parental strands must unwind and separate permanently into single stranded state. It is a complex multistep process involving many enzymes. Mechanism of DNA replication is the direct result of DNA double helical structure proposed by Watson and Crick. Maintenance of integrity of genetic information is the main feature of replication. Similarly, if there is cytosine in the parent strand, complementary guanine will be copied into the new daughter strand. If there is adenine in the parent or old strand, complementary thymine will be added to the new strand. The base sequence of parent or old strand directs the base sequence of new or daughter strand. Each strand functions as a template for the new complementary daughter strand. The two strands uncoil and permanently separate from each other. This specific complementary base pairing provides the mechartism for the replication. Adenine of one strand pairs with thymine of the opposite strand and guanine pairs with cytosine. The two strands have complementary base pairing. Therefore the main role of replication is to duplicate the base sequence of parent DNA molecule. Basic Features of DNA Replication:Īll genetically relevant information of any DNA molecule is present in its sequence of bases on two strands. DNA molecule must be uncoiled and the two strands must be separated for the replication process. This imposes several restrictions on DNA replication. DNA molecule is coiled and twisted and has enormous size. Genetic information present in double stranded DNA molecule is transmitted from one cell to another cell at the time of mitosis and from parent to progency by faithful replication of parental DNA molecules. But sometimes RNA acts as a template for DNA synthesis (reverse transcription), Example is RNA viruses (HIV virus). Proteins never serve as template for RNA synthesis. In 1956 Francis Crick called this pathway of flow of genetic information as the Central Dogma.īoth transcription and translation are unidirectional. The RNA then synthesizes proteins, which are specific sequence of amino acids, by a process called translation. This information (genetic code) is for specific sequence of amino acids. This information is copied and transcribed into RNA molecules. This information is in the form of nucleotide sequence called genetic code.
DNA is the storehouse of genetic information.
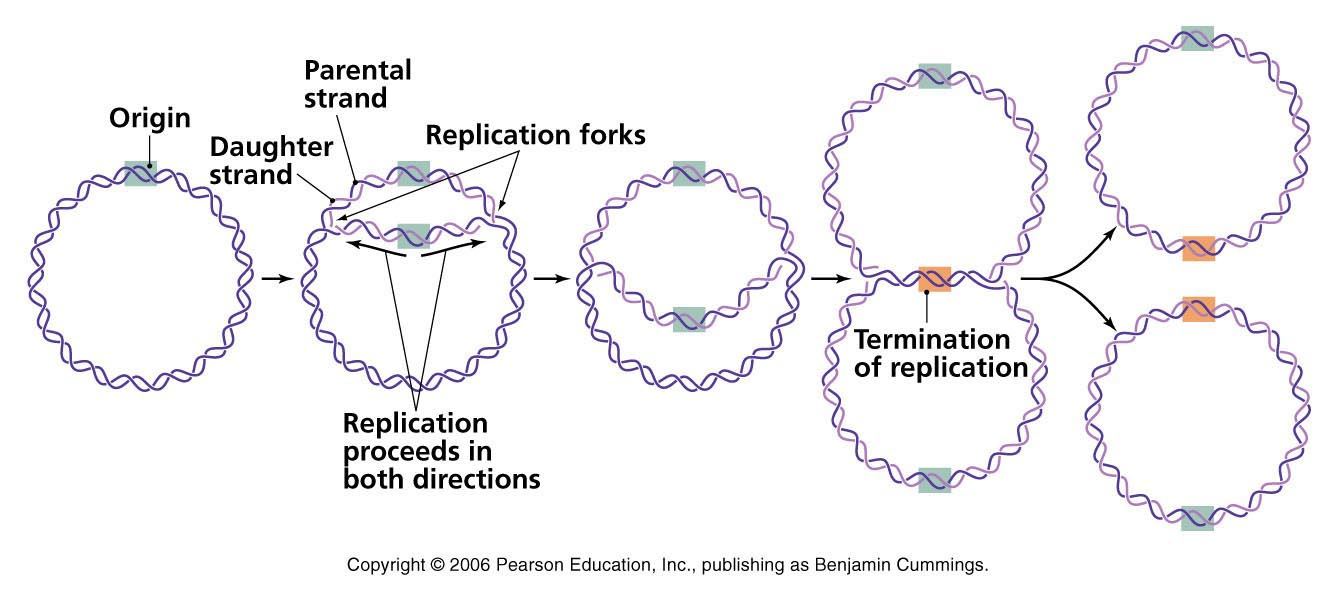
Genetic material is always nucleic acid and it is always DNA except some viruses. Formation of Replication Forks & Replication Bubbles and Others. Let us make an in-depth study of the DNA replication:- Learn about: 1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
